Dispersion of light












Dispersion of Light
We see colours all around us. The blue sky, green leaves, red roses, yellow sunflowers, colourful birds and butterflies, etc., are just some of the colours we see in nature. And then we have the colours of our clothes, pens, pencils, houses, vehicles, and so on. The colours we see depend on the colour of light entering our eyes from an object or a source of light. Different sources of light may produce lights of different colours. A sodium-vapour lamp, for example, produces a yellowish light. The flame of a gas stove emits blue light. But sunlight does not appear to have a colour. The same is true of certain types of bulbs we use at home. We call such light (i.e., those that appear colourless) white light.
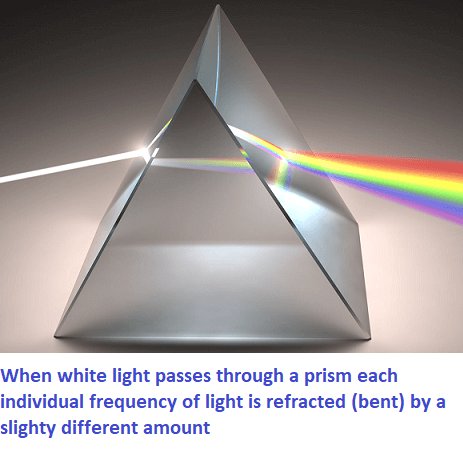
Though white light does not appear coloured, it is actually a mixture of lights of different colours present in a definite proportion. Lights of different colours have different wavelengths. So, they behave differently. For example, they travel at different speeds. This makes the refractive index of a transparent material slightly different for different colours of lights. So, lights of different colours bend by different amounts on refraction. Therefore, under certain conditions, when white light gets refracted, its components bend by different amounts and separate out. You must have seen this happen when sunlight passes through a glass of waterfalls on the table or the floor, producing a band of colours. The phenomenon of splitting light into its component colours due to the dependence of refractive index on wavelength is called the dispersion of light.
How many colors is white light made up of ? | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
An example of dispersion of light in nature ______________ . | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
The phenomenon of scattering of light by colloidal particles is known as ________.
| |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
I have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.
